How to Build a Local Business Directory Using Yelp Data: Complete 2025 Guide

Building a local business directory isn’t just about aggregating data—it’s about creating a resource that genuinely serves your community while generating sustainable revenue. I’ve watched countless entrepreneurs rush into directory projects, eager to tap into Yelp’s massive database, only to stumble over compliance issues, data quality problems, or fundamental misunderstandings about what makes a directory valuable.
Here’s what most guides won’t tell you: the real challenge isn’t accessing Yelp data (that part’s actually straightforward). The challenge is building something differentiated enough to attract users while staying within Yelp’s terms of service. You’re walking a tightrope between leveraging existing data and creating genuine value that justifies your directory’s existence.
This guide cuts through the theoretical nonsense and focuses on practical implementation. Whether you’re a developer looking to build from scratch or a business owner considering a turnkey solution, you’ll find actionable strategies for creating a compliant, profitable local business directory.
TL;DR – Quick Takeaways
- Yelp data access requires API compliance – Real-time integration with proper attribution is mandatory, no scraping allowed
- Differentiation is critical – Focus on niche targeting, geographic specialization, or unique features Yelp doesn’t offer
- Data freshness matters – Implement automated update schedules and quality checks to maintain accuracy
- Multiple revenue streams work best – Combine featured listings, subscriptions, and affiliate partnerships
- Mobile-first design is non-negotiable – 76% of local searches happen on mobile devices
- Real-time API calls avoid legal issues – Don’t cache Yelp data long-term unless explicitly permitted
Understanding the Yelp Data Ecosystem and API Landscape
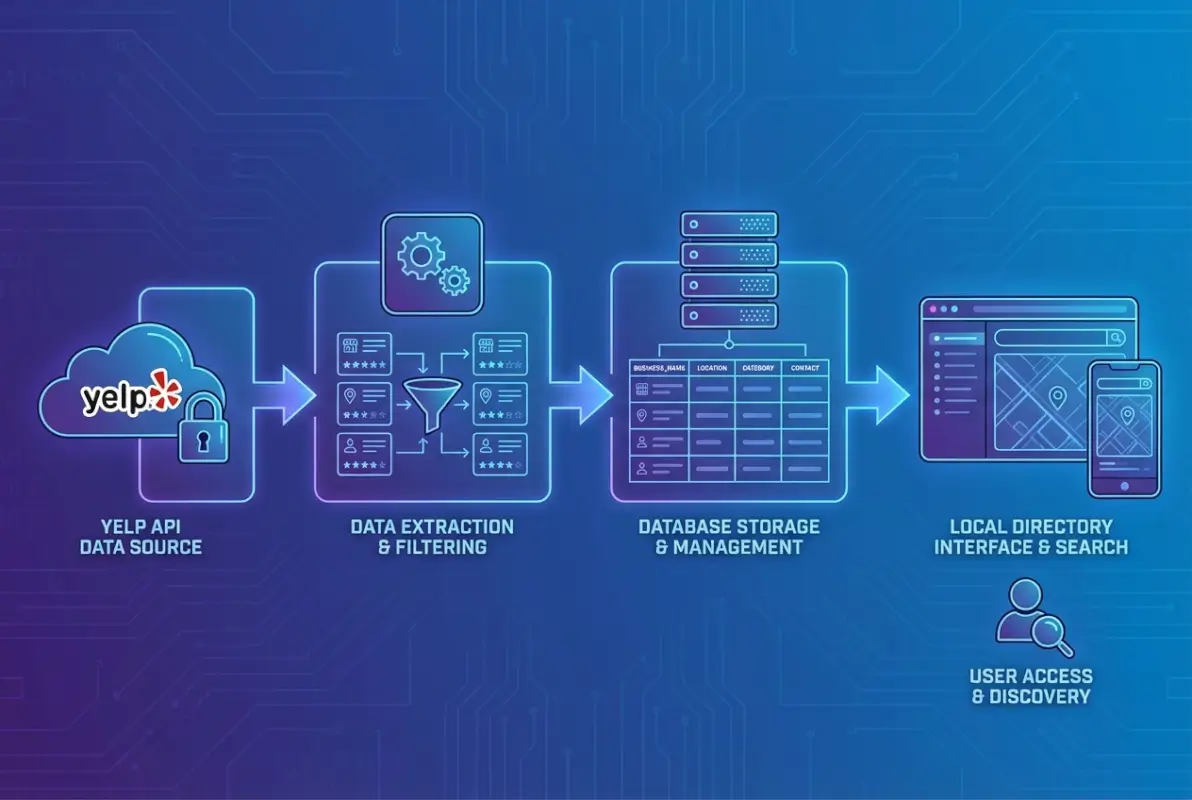
The Yelp Fusion API represents your legitimate gateway to business data covering millions of establishments. Unlike web scraping (which violates their terms and can result in legal action), the API provides structured, reliable access to business information, ratings, reviews, and operational details.
The Yelp Data Ingestion API offers several endpoints tailored for different use cases. Business Search lets you query by location, category, and various filters. Business Details provides comprehensive profiles including hours, attributes, and contact information. The Reviews endpoint delivers review excerpts (not full reviews, which remain on Yelp’s platform). Phone Search enables lookups via phone number, while Autocomplete powers search-as-you-type functionality.
Rate limits present the first major constraint you’ll encounter. Yelp enforces daily query caps that vary based on your agreement level. For most developers starting out, expect limits around 5,000 API calls per day on the free tier. This sounds generous until you realize a single user session might trigger multiple API calls for search results, business details, and reviews.
Critical Compliance Requirements You Cannot Ignore
Yelp’s terms of service include several non-negotiable requirements. Attribution must appear prominently—you’re required to display the Yelp logo and clearly indicate when data originates from their platform. This isn’t optional or negotiable.
The no-competing-service clause causes confusion for many developers. Yelp explicitly prohibits creating services that directly compete with their core offering. This means you can’t simply build “Yelp 2.0” with their data. Your directory must offer distinct value: geographic specialization (focusing on a specific city or region), vertical focus (targeting specific industries like restaurants, healthcare, or home services), enhanced features (adding capabilities Yelp doesn’t provide), or complementary data (enriching Yelp information with additional sources).
I learned this the hard way during a consulting project where a client wanted to cache all business data for faster page loads. After reviewing Yelp’s terms with their legal team, we restructured the entire architecture around real-time calls with aggressive CDN caching for non-Yelp elements instead.
Current Local Search Behavior and Market Dynamics
Local search has fundamentally transformed how consumers discover businesses. Understanding these patterns helps you design a directory that aligns with actual user behavior rather than theoretical assumptions.
According to BrightLocal’s Consumer Review Survey, 87% of consumers read online reviews for local businesses, with 79% trusting online reviews as much as personal recommendations. This trust factor explains why review data remains central to any successful directory.
Mobile dominance has reached a tipping point. Roughly 76% of people who search for something nearby on their smartphone visit a related business within a day, and 28% of those searches result in a purchase. Your directory absolutely must deliver a flawless mobile experience—not as an afterthought, but as the primary design focus.
| Search Type | Conversion Rate | Avg. Decision Time |
|---|---|---|
| Near me searches | 28% | 24 hours |
| Category searches | 18% | 2-3 days |
| Specific business name | 64% | Same day |
Where Yelp Fits in the Local Discovery Ecosystem
Yelp processes approximately 178 million unique visitors monthly across their platform. Their local search data solutions demonstrate the platform’s reach, but also reveal opportunities for specialized directories.
Yelp excels at broad coverage and user-generated reviews. However, their general-purpose approach creates gaps: industry-specific features and terminology, hyper-local neighborhood focus, specialized filtering for niche audiences, integration with industry-specific tools, and curated recommendations beyond algorithmic ranking.
These gaps represent your opportunities for differentiation. A directory focused exclusively on healthcare providers could integrate appointment booking and insurance verification—features Yelp doesn’t prioritize. A neighborhood-specific directory might include historical context, community events, and local advocacy information alongside business listings.
Architecting a Compliant Directory with Real-Time Yelp Integration
The technical architecture of your directory determines both its compliance posture and its scalability potential. Poor architectural decisions made early can haunt you for years (ask me how I know).
When add database business directory website, your data model needs to separate Yelp-sourced data from your proprietary information. This separation serves both legal compliance and practical flexibility.

Real-Time API Integration vs. Data Enrichment Models
You have two primary architectural patterns to consider. Pure real-time integration means every user search triggers live API calls to Yelp. This approach maximizes data freshness and minimizes compliance risks, but introduces latency and API quota concerns.
The hybrid enrichment model stores your own business data while pulling Yelp-specific elements (ratings, reviews) in real-time. This balances performance with compliance, assuming you’re building your core dataset from legitimate sources beyond Yelp.
Your database schema should include separate tables or collections for: core business information (your proprietary data), Yelp metadata (IDs, last sync timestamps), cached API responses (with strict TTL enforcement), user-generated additions (photos, tips, local insights), and business owner claims and verifications.
Data Freshness Strategies That Actually Work
Stale data kills user trust faster than almost any other directory sin. Nobody wants to call a business based on your listing only to discover it closed six months ago.
Implement a tiered update schedule: high-traffic listings update daily (businesses with 50+ monthly views), medium-traffic listings update weekly (businesses with 10-49 monthly views), low-traffic listings update monthly (businesses with fewer than 10 views), and new listings get immediate validation upon addition.
Change detection becomes critical at scale. Rather than blindly updating everything, compare API responses against cached data and only update when changes occur. This conserves API quota and database write operations.
Building High-Performance Search and Discovery Features
Search functionality makes or breaks a business directory. Users arrive with intent—they’re looking for something specific—and your search needs to deliver relevant results instantly.
Basic database queries (LIKE statements in SQL) simply don’t scale or deliver the relevance users expect. This is where dedicated search technology like Elasticsearch becomes essential.

Implementing Elasticsearch for Business Discovery
Elasticsearch provides full-text search with relevance scoring, fuzzy matching for typos and variations, geospatial search capabilities, faceted filtering, and the performance to handle millions of records with sub-200ms response times.
Your Elasticsearch index should map business data with appropriate field types: business name (text with keyword subfield for exact matches), description (text analyzed for full-text search), categories (keyword for exact filtering), location (geo_point for proximity searches), rating (float for range filtering), and review_count (integer for sorting and filtering).
Field boosting dramatically improves relevance. Boost business name matches higher than description matches, category matches higher than generic content, and recently updated listings slightly over stale ones.
Location-Based Filtering That Users Actually Want
Location is often the most important search criterion for local directories. Users think in terms of neighborhoods, landmarks, and convenience rather than precise coordinates.
Your location handling should support: current location detection (with permission), radius-based filtering (“within 5 miles”), neighborhood selection (requires boundary data), landmark-based searches (“near City Hall”), and map-based area selection (drawing or clicking regions).
Geocoding accuracy matters more than you’d think. An address like “123 Main St” might exist in dozens of cities. Always require city/state context and validate coordinates against expected boundaries.
Creating a Directory Interface That Converts Visitors
A powerful backend means nothing if users bounce because your interface confuses or frustrates them. User experience design requires understanding how people actually search for local businesses—not how you think they should search.
When how to start business directory step by step guide, interface design should come after you’ve mapped user journeys based on real behavior patterns.

Mobile-First Design Principles for Local Discovery
Designing for mobile first isn’t just responsive design—it’s rethinking the entire experience for context-aware, on-the-go users. Someone searching for “plumber near me” on their phone at 8 PM likely has an emergency. Your interface should prioritize: click-to-call buttons (prominently displayed), directions/navigation (one-tap access to maps), “open now” filtering (surfaced by default), quick-view business cards (essential info without navigation), and minimal form fields (autofill everything possible).
Touch targets must measure at least 44×44 pixels—smaller elements lead to mis-taps and frustration. Space interactive elements appropriately and test on actual devices, not just browser simulators.
| Element | Desktop Priority | Mobile Priority |
|---|---|---|
| Phone number | Secondary | Primary (click-to-call) |
| Full address | Always visible | Collapsed (tap for directions) |
| Business hours | Expandable | “Open now” badge only |
| Reviews | Previewed | Rating + count (tap for details) |
Map Integration and Location Visualization
Map views provide spatial context that lists simply cannot. The Google Maps API enables interactive exploration, but requires careful implementation to control costs.
Your map integration should offer: synchronized list and map views (hovering over a listing highlights its marker), clustering for areas with high business density, custom markers for different categories, “search this area” when users pan or zoom, and info windows with key details on marker click.
Google Maps pricing operates on a pay-per-use model. Map loads, geocoding requests, and Places API calls each count toward your monthly bill. According to Google Cloud’s pricing structure, implementing strategic caching and lazy-loading can reduce costs by 40-60%.
Monetizing Your Directory Without Destroying User Experience
A directory that doesn’t generate revenue won’t survive long enough to serve its community. However, aggressive monetization that prioritizes revenue over user experience destroys the trust that makes directories valuable in the first place.
The question isn’t whether to monetize—it’s how to do so ethically and sustainably.
Featured Listing Models That Work
Featured listings represent the most straightforward revenue stream. Businesses pay for enhanced visibility and richer profiles. When how much to charge for featured business directory listings, consider the value you’re delivering.
Tiered pricing creates options for businesses of different sizes: basic featured listings ($50-100/month) include top placement in search results, a “featured” badge, and priority in category pages. Professional listings ($150-300/month) add enhanced profiles, additional photos, social media integration, and priority customer support. Premium listings ($500+/month) offer category exclusivity, homepage features, detailed analytics, and lead tracking.
Transparency matters enormously. Clearly label featured listings and never manipulate organic results to force businesses into paid tiers. Users need to trust that your free listings represent genuine search relevance.
Alternative Revenue Streams Beyond Featured Listings
Diversification protects your directory from over-reliance on any single revenue source. Successful directories often combine: featured listings (primary revenue), affiliate commissions (booking platforms, service providers), lead generation fees (qualified leads for high-value services), advertising (display ads, sponsored content), premium tools (enhanced analytics for business owners), and directory services (profile creation, photography, content writing).
When evaluating pricing preschool business directory listings versus other industries, recognize that customer lifetime value varies dramatically. A single customer for a preschool might represent $15,000+ in tuition over several years, while a restaurant customer might spend $30. Price your featured listings according to the value businesses receive.
Maintenance, Quality Control, and Long-Term Sustainability
Launching your directory is just the beginning. Long-term success requires systematic maintenance, quality monitoring, and continuous improvement based on real usage data.
Automated Update Systems and Data Quality
Manual updates don’t scale beyond a few dozen listings. Implement automated systems using cron jobs or scheduled tasks to handle: daily updates for high-traffic listings (ratings, reviews, hours), weekly refreshes for active businesses (contact info, basic details), monthly audits for low-traffic listings (existence verification, major changes), and quarterly deep updates (comprehensive data refresh, photo updates).
Your automation should include error handling, retry logic, and alerting for persistent failures. Nothing’s worse than discovering your update script has been silently failing for weeks.
User Feedback and Community Engagement
Your users encounter data problems before you do. Create simple mechanisms for reporting issues: “Report incorrect information” buttons, business owner claim processes, community-submitted photos and tips, and flagging systems for closed or moved businesses.
Respond to feedback promptly. Set service-level targets: critical issues (closed business, wrong location) within 24 hours, important updates (hours, contact info) within 3 days, and minor corrections (description edits, category adjustments) within 1 week.
Using proven tactics advertise business directory helps you maintain growth while improving quality through community engagement.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I legally use Yelp data to build my own business directory?
Yes, but only through Yelp’s official API with strict compliance requirements. You must properly attribute Yelp, follow their display guidelines, avoid long-term caching, and ensure your directory doesn’t directly compete with Yelp’s core service. Scraping Yelp’s website violates their terms and can result in legal action.
What are the main limitations when using Yelp’s API for a directory?
Key limitations include daily rate limits (typically around 5,000 calls for standard access), restrictions on data caching, attribution requirements, limited review access (excerpts only), and terms prohibiting competing services. You’ll need to design around real-time API calls rather than maintaining a complete cached database.
How should I properly attribute Yelp data on my directory pages?
Display the Yelp logo prominently near Yelp-sourced content, clearly label ratings and reviews as coming from Yelp, link back to the business’s Yelp page, and follow Yelp’s specific branding guidelines. Attribution isn’t optional—it’s a legal requirement under their terms of service.
Is it legal to cache Yelp data to improve my directory’s performance?
Short-term caching for performance optimization may be acceptable (check current terms), but long-term database storage of Yelp data generally violates their terms. Focus on real-time API integration with CDN caching for static elements and implement efficient query patterns to minimize API calls.
What other data sources can I combine with Yelp data?
Supplement Yelp with Google Business Profile data, municipal business licenses, industry-specific databases, user-generated content, business owner submissions, proprietary research, and niche-specific information sources. This creates differentiated value beyond what Yelp alone provides.
How can I differentiate my directory from Yelp itself?
Focus on geographic niches (specific cities or neighborhoods), vertical specialization (particular industries), enhanced features (booking systems, pricing tools, detailed filters), curated recommendations, community integration, or complementary services that Yelp doesn’t prioritize. Differentiation is essential for both compliance and competitive success.
What technology stack works best for building a Yelp-powered directory?
Popular options include WordPress with directory plugins for quick deployment, React/Node.js for custom high-performance applications, or frameworks like Laravel or Django for developers comfortable with those ecosystems. Your choice depends on technical expertise, scalability requirements, and customization needs.
How much does it cost to build and maintain a business directory?
Basic directories start around $500-1,000 for DIY WordPress solutions. Custom development ranges from $5,000-50,000 depending on complexity. Ongoing costs include hosting ($10-200+/month), API fees (Google Maps, potentially Yelp if you exceed free tiers), maintenance, and content updates. Budget accordingly for both initial development and ongoing operations.
What’s the best way to handle API rate limits at scale?
Implement intelligent caching strategies, prioritize updates for high-traffic listings, use change detection to avoid unnecessary API calls, implement request queuing and throttling, consider upgrading to higher API tiers as you scale, and design your architecture to batch requests efficiently.
Should I allow business owners to edit their own listings?
Yes, implement a claim and verification process that lets business owners prove ownership and update their information. This improves data accuracy while reducing your maintenance burden. Require verification (email, phone, documentation) before granting edit access, and maintain audit trails of all changes.