How to Hide Plugins in WordPress: 5 Simple Methods for Admins
When I first started managing WordPress sites, I was amazed by how cluttered the admin dashboard could become with dozens of plugins listed everywhere. The constant visual noise from plugin notifications, menu items, and dashboard widgets wasn’t just distracting – it was creating real security risks as team members accidentally clicked on settings they shouldn’t touch. Learning how to hide plugins in WordPress became one of my most valuable admin skills, not because I wanted to remove functionality, but because I needed to create cleaner, safer admin experiences for different user roles.
TL;DR – Quick Takeaways
- UI-Level Hiding – Hide plugins from view without deactivating them using specialized filtering plugins
- Role-Based Control – Show different plugins to different user roles for better security and workflow management
- Admin Menu Filtering – Remove plugin-related menu items and dashboard clutter for cleaner interfaces
- Security Hygiene – Hiding plugins improves UX but real security comes from proper updates and removal of unused plugins
- Reversible Methods – All hiding techniques can be quickly undone without affecting plugin functionality
The need to hide plugins typically stems from three core scenarios: maintaining security hygiene by reducing accidental modifications, creating cleaner admin interfaces for non-technical users, and implementing proper access control in multi-user environments. Unlike directory listings that need maximum visibility, your WordPress plugin list benefits from strategic concealment.
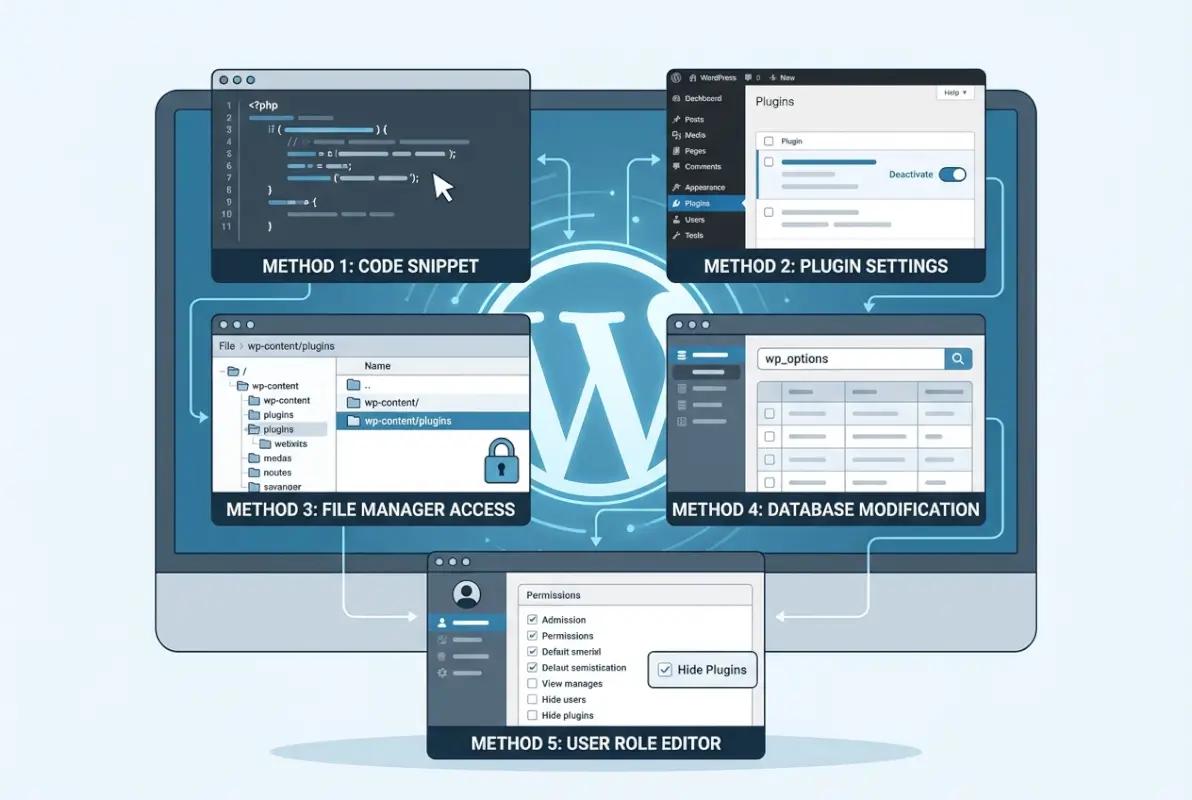
Method 1: Use Admin Plugin Filtering Tools
The most straightforward approach involves installing a dedicated plugin that filters which plugins appear in your admin interface. These specialized tools create a layer between your actual plugin installations and what users see in the WordPress dashboard.
Popular options like WP Plugin Filter allow you to selectively hide plugins from the main Plugins screen while keeping them fully functional. The process involves installing the filtering plugin, accessing its settings panel, and choosing which plugins to hide from specific user roles or all users except administrators.
The key advantage of this method is its granular control – you can hide plugins from editors while keeping them visible to administrators, or create completely custom visibility rules based on user capabilities. Some advanced filtering plugins even support multisite networks, allowing you to manage plugin visibility across multiple WordPress installations from a central dashboard.
When implementing plugin filtering, document which plugins you’ve hidden and why. This documentation becomes crucial when onboarding new administrators or troubleshooting issues months later. The hidden plugins remain fully active in your site’s functionality – they’re simply invisible in the admin interface.
Method 2: Hide Admin Menus and Dashboard Elements
Rather than hiding plugins themselves, this approach focuses on removing the menu items and dashboard elements where plugin settings typically appear. By strategically hiding admin menu sections, you can reduce plugin visibility without directly filtering the plugins list.
Admin menu hiding plugins like Hide Admin Menu provide comprehensive control over which dashboard sections appear for different user roles. You can hide the entire Plugins menu from editors, remove specific plugin settings pages from the admin sidebar, or even hide plugin-related items from the admin toolbar that appears on the front end of your site.
This method proves particularly effective for SEO-focused sites where you want to prevent content creators from accidentally modifying critical optimization plugins. By hiding the relevant menu items, you maintain plugin functionality while preventing unauthorized access to sensitive settings.
| Hiding Approach | Visibility Level | Complexity | Reversibility |
|---|---|---|---|
| Plugin List Filtering | Plugins page only | Low | Instant |
| Admin Menu Hiding | Entire dashboard | Medium | Quick |
| Role-Based Control | User-specific | High | Moderate |
The configuration typically involves selecting which menu items to hide and specifying the user roles affected by these changes. Most admin menu hiding plugins provide preview modes, allowing you to see how the dashboard will appear to different user types before implementing the changes permanently.
Method 3: Reduce Dashboard Clutter with Notice Management
Plugin-related dashboard clutter often comes from notifications, update notices, and promotional messages rather than the plugins themselves. Managing these elements can significantly reduce the visual prominence of certain plugins without affecting their core functionality.
Tools like Disable Admin Notices provide comprehensive control over the various notifications that plugins display in your WordPress dashboard. This approach focuses on cleaning up the admin experience rather than hiding plugins directly, but the result is often more effective for reducing distractions and accidental interactions.
The strategy works particularly well when combined with business listing optimization workflows where multiple team members need access to content management tools without being overwhelmed by technical plugin notifications.
When implementing notice management, create categories for different types of plugin communications. Critical security alerts should always remain visible, while promotional notices about premium features can be safely hidden. Some advanced notice management plugins even allow you to redirect important notifications to specific administrator email addresses instead of displaying them in the dashboard.
Method 4: Control Front-End Admin Toolbar Visibility
The WordPress admin toolbar appears on the front end of your site when administrators are logged in, often displaying plugin-related shortcuts and information. Controlling this toolbar’s contents can significantly reduce plugin visibility during front-end work.

Front-end toolbar management involves both hiding specific plugin elements from the admin bar and controlling which user roles can see toolbar elements at all. Many plugins add their own shortcuts to this toolbar, creating visual clutter that can distract from content editing and site preview tasks.
This method proves especially valuable for sites where content creators work primarily on the front end, such as when using page builders or managing featured listings that require visual editing. By streamlining the toolbar, you create cleaner work environments while maintaining plugin functionality.
Modern toolbar management plugins allow granular control over individual toolbar elements, including plugin-specific items, WordPress core tools, and custom additions. You can create different toolbar configurations for different user roles, ensuring that each team member sees only the tools relevant to their responsibilities.
Method 5: Implement Role-Based Plugin Visibility
The most sophisticated approach to hiding plugins involves creating comprehensive role-based access control systems that determine not just who can activate or deactivate plugins, but who can even see that they exist.

Role-based plugin visibility requires careful capability mapping to ensure that hiding plugins doesn’t accidentally prevent users from accessing necessary functionality. The approach typically involves using user role management plugins that extend WordPress’s built-in capability system with more granular controls.
This method becomes essential for enterprise WordPress installations or agency environments where multiple clients or team members need different levels of access to plugin management. Similar to how marketplace sellers manage different listing tools, different WordPress users need different plugin access levels.
Implementation involves mapping out user workflows, identifying which plugins each role needs to see, and configuring the visibility rules accordingly. Advanced role management plugins often integrate with membership systems, allowing you to create complex permission hierarchies that scale with your organization’s needs.
Advanced Method: Programmatic Plugin Hiding
For developers and advanced administrators comfortable with code modifications, WordPress provides several hooks and filters that allow direct manipulation of the plugins list display. This approach offers maximum control but requires ongoing maintenance and careful testing.
The most common programmatic approach involves filtering the `all_plugins` array to remove specific plugins from the admin interface. This method requires adding custom code to your theme’s functions.php file or creating a custom plugin specifically for plugin management.
While this approach provides ultimate flexibility, it’s generally recommended only for developers who understand the implications of modifying WordPress core functionality. Most administrators will find the plugin-based solutions more reliable and easier to maintain over time.
Security and Best Practices Considerations
Hiding plugins should complement, not replace, proper WordPress security hygiene. The most important security practice remains regularly auditing your installed plugins and removing any that aren’t actively needed for your site’s functionality.
Real security comes from keeping WordPress core and all plugins updated, using strong authentication methods, and following established security protocols. According to WordPress.org’s official security guidelines, maintaining updated software provides far more protection than obscuring plugin installations.
When implementing any plugin hiding strategy, establish clear documentation processes so that future administrators can understand and modify your visibility rules. This documentation should include which plugins are hidden, why they’re hidden, and how to access them when necessary.
Regular testing across all user roles ensures that hiding plugins doesn’t interfere with necessary workflows. Schedule quarterly reviews of your plugin visibility settings to ensure they still align with your team’s needs and site functionality requirements.
Frequently Asked Questions
Do hiding plugins affect site security or plugin functionality?
No, hiding plugins only affects their visibility in the WordPress admin interface. Hidden plugins remain fully functional and continue running normally. However, hiding plugins doesn’t improve security – proper updates and removal of unused plugins are still essential for maintaining site security.
Is hiding plugins the same as uninstalling them?
Absolutely not. Hiding plugins only removes them from view in the admin dashboard while keeping them active and functional. Uninstalling completely removes the plugin files and deactivates all functionality. Hidden plugins still consume server resources and require maintenance.
Will hiding plugins confuse other admins or users?
It can, which is why documentation is crucial when implementing plugin hiding. Always maintain clear records of which plugins are hidden and provide instructions for accessing them. Consider creating different visibility rules for different user roles to minimize confusion.
Can I hide plugins differently for different user roles?
Yes, most plugin hiding solutions support role-based visibility controls. You can show all plugins to administrators while hiding specific plugins from editors, authors, or custom user roles. This approach provides flexible access control based on user responsibilities and technical expertise levels.
Are there any risks to hiding plugins using UI tweaks?
The main risk is forgetting about hidden plugins during maintenance tasks like updates or troubleshooting. Hidden plugins can also make it difficult to identify conflicts or performance issues. Always maintain documentation and consider the long-term maintenance implications of your hiding strategy.
How do I test hiding plugins safely on a staging site?
Create a complete copy of your live site on a staging environment, implement your plugin hiding configuration, then test all user workflows with different role accounts. Verify that hidden plugins remain functional and that users can still access necessary features before applying changes to your live site.
Will hiding plugins affect my site’s performance?
Plugin hiding typically has minimal impact on site performance since most methods only affect admin interface display. Some hiding plugins add minor overhead, but this is usually negligible. The hidden plugins themselves continue running normally and consume the same server resources as visible plugins.
Can I quickly revert plugin hiding if something goes wrong?
Yes, most plugin-based hiding solutions can be quickly reversed by disabling the hiding plugin or changing its configuration settings. However, if you use programmatic methods or complex role-based systems, reverting changes may require more technical steps, which is why staging site testing is important.
Should I hide plugins from all users or just specific roles?
The best approach depends on your site’s management structure. Generally, keep plugins visible to administrators and developers who need full access for maintenance, while hiding them from content creators, editors, and other non-technical users who don’t need plugin management capabilities.
What’s the difference between hiding plugins and restricting plugin activation rights?
Hiding plugins affects visibility in the admin interface while keeping plugins functional. Restricting activation rights prevents users from activating or deactivating plugins but doesn’t hide them from view. You can combine both approaches for comprehensive plugin access control in multi-user environments.
Managing plugin visibility in WordPress requires balancing user experience, security considerations, and workflow efficiency. The methods outlined above provide practical solutions for reducing admin interface clutter while maintaining full plugin functionality. Remember that the goal isn’t to achieve perfect invisibility, but rather to create cleaner, safer admin environments that reduce accidental modifications and improve focus on essential tasks.
The most effective approach often combines multiple methods – using plugin filtering for basic visibility control, role-based access for user management, and notice suppression for dashboard cleanup. Whatever combination you choose, prioritize documentation and regular testing to ensure your hiding strategy enhances rather than complicates your WordPress management workflow.
Start with the simplest plugin-based solutions before moving to more complex programmatic approaches. Your future self (and any administrators who come after you) will appreciate the thoughtful balance between functionality and visibility that makes WordPress administration both safer and more efficient.